Knee
Colgan Osteopath in Kettering Northamptonshire
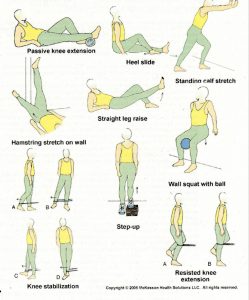
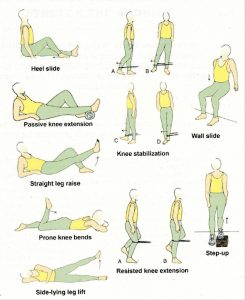
Knee exercise
Meniscal tear
MCL sprain
Knee pathologies
Meniscal tear
medial 75%, lat 25%. MCL attached to med meniscus, LCL not attached to lat men. no nerves in menisci but a lot in transition zone b/n men and capsule. weight 50%standing, 90%with knee flexed, male X3>fem. tears 1. trauma, 2. degenerative. risk – ligament laxaty, deep knee bent, repetitive rotation force. SSx – joint line P, locking, catching, swelling, +/-Bakers, incr P on hyperflexion/hyperextension, decr ROM on extension, often P at night, DDx joint mice
Infrapatellar tendinitis ( jumper knee)
degenerative tendinopathy of infrapatellar tendon (Often together with chondromalacia patella) due to overuse. Risk: overpronation, structural (e.g. patella alta, genu varus/valgus, leg length), mm imbalance – VMO vs ITB + Vas. Lat. Maintaining – weight lifting, hill training. SSx – P ant knee (esp after activity), +ve movie sign, P when arising from sitting, P on palpation. DDx – (<16) Osggood, bursitis, chondromalacia (grinding)
Chondromalacia patella
erosion of articular surface of patella due to repetitive stress, Q angle, mm imbalance, anatomical (pat alta or bassa). Risk – pronation (incr LSp lordosis), tight ITB. SSx – incr P going down stairs, kneeling, prolonged sitting, crepitis. DDx – jumpers knee (no crepitis), meniscus, bursitis
MCL sprain
injury on lat rot of femur on tibia or valgus force. grade 1 mild (no laxaty, but P) <6mm gapping. SSx P & swelling on med knee. DDx – med meniscus, ACL, PCL, pes anserinus
ACL sprain
attached to ant tib and lat condyle femur. highest rate during ovulation, hypermobility. pronation syndrom (incr pronation led int rot of tibia led incr tension on ACL). Unhappy triad – ACL, MCL, med menis. valnerable in all rotation (int & ext), hyperextension, valgus force and hit from behind. SSx may dissapear in several weeks but lig takes up to 1 year to regain strength
PCL sprain
post tibia and med condyle of femur. x2 stronger than ACL, stabilise post shift of tibia. Risk – hit dashboard, collision sport. tibia translation <1 cm – conservative. ttt > 1cm – surgery. Test – post drawer (back into normal position). if untreated – 4-5 years OA + meniscal
LCL sprain
least frequent of 4 ligs. – ACL 50%, MCL 40%, PCL 7%, LCL3%. Best palpated in Zikov position. grade 1 & 2 no gapping at 0 degree and 30 degree, 3 – gapping. Prognosis 1 – 6/52, 2-nd grade 12/52
Pes Anserinus tendinopathy (& bursitis)
cause: too much lat tibial rot, over pronation, direct pressure on med knee (motorbike, roofer). SSx pin point P at bursa, incr P with running (may be able to run through P, but worse after), warm.
ITB syndrome
irritation and inflammation of distal ITB (bursa may be swallen) due to overuse. Tibial attachment of ITB is Gerby’s tubercle and superiorlateral patella. Tension of ITB – post Glut Max, ant TFL. Risk – over/ under pronation, valgus/varum (gives anatomicaly thicker ITB), leg lenth, bicycle seat too high. SSx – P diffuse lat (esp going downhill). Test – Renne test (palpation while rising on chair or squating)
Baker`s cyst (also known as popliteal bursitis, gastrocnemius bursitis)
inflam of bursa post to knee (it communicate with join cavity). not always visible. Causes 1. irritation from gastrocs, poplitius or/and semimembranosis 2. int knee joint derangement, OA, meniscus. joint infl – overfill – goes to bursa. SSx – can not flex knee fully, incr P at the end of flexion. incr P when strenghtening leg after prolonged sitting. DDx – popliteal aneurism (pulsating mass), fat, tumor. ttt – cyst aspiration and filling it with corticosteroid
Popliteal tendinitis
Inflam of popliteal tendon often due to running downhill. SSx – P when running downhill in post knee. DDx – menisci . ttt – rest, NSAIDs, ice, no downhill running for 6/52
Osgood`s – Schlatter disease
Traction lesion due to excersive pull of patellar lig on tib apophysis. Ptn male 10-15, U/L P, swelling, hypertrophy of tib tuberosity. ttt – P relief, avoiding sport with deep bending untill 16. Prognosis – spontaneous resolution after course of weeks or months
Sindling-Larsen-Johanson
Traction epiphysitis of inferior pole of patella. often with calcification if chronic in adult. ptn 8-16 or adult athlet running and squating. SSx P on palpation, no crepitis, no swelling. in teenage resolves spontaneously with rest
Fat pad impingement (Hoffa’s pad)
P in the eyes of knee on palp. P on hyperextension in ant knee. Hx of trauma and hyperextension. ttt – PRICE, avoid P-full activities
Plica syndrome
Prepatellar bursitis
Quads tendinitis (distal patella)
Osteochondritis
separation of subchondrial bone and art cartilage from end of bone that extrudes fragment into joint cavity. age 11-20, Hx of overuse. SSx – joint locking / crepitis, P agg by balistic activities, myospasm. ttt – mobilization is contraindicated. osteochondrosis if no inflamation
RED FRIC 3 REF
Vascular – popliteal aneurysm
“Fracture” – stress # of tibia, meniscus tear, osteochondritis
Rheumatic- OA, (RAPE – RA, Ankispon, Psoriatic, enteropathic A (fem with Chron or Ulc.C.)), Reiters (yong male), Vessels, Nerves and Cristalls: SLE (90% joints), pseudogout (CPPD- old fem, Ca2O7P2 calcium pirophosphat deposit), chondrocalcinosis – chronic pyrophosphate arthropathy
Infection – septic A, osteomyelitis
Cancer – osteosarcoma (<30), osteochondroma (ptn 10-30 yo)
Referral –
1.biomech – from hip (medial knee), ankle
2. neural – L3, saphenous N (entrapted between Adductor magnus and vastus medialis (bodybuilders) or while penetrating pes anserinus tendon), common peronial N (excessive icing), obturator N, femoral N.
Knee Exam
I am going to examen your knee, this involves having a look, a feel and asking you to do a few exercise
Gait– symmetry, antalgic
Observation –
standing–
front- alighment. varus, valgus, q angle, mm waist (vastus medialis)
side – recurvatum
posterior – baker cyst, popliteal aneurism
feet – cavus, planus (PFPS), big toe
supine – skin, scars, colore, temperature, swelling
Active movement – bend and straight
Passive movement – now i will do the same movement but i need you to relax and let me take the full weight of your leg- can you make your leg go nice and floppy
flex, extend, rotate
look for hyperextension (>5grad) and feel for crepitus
General Palpation
- tibial tubercle-osgood schlatter
- infra patelar lig – jumpers knee
- fat pad- press for pain
- joint line – meniscus, OA,
- border of patella
- quads tendon
- popleteal fossa – baker cyst, aneurism
medial 8. MCL
9. pes anserinus
lateral 10. ITB syndrome (fem condyle)
11. LCL femcondyle – tibial head
12. tibial femoral join

Patella
1. tracking + crepitis with passive movement
2. stability – side to side
3. patella tap 1. move fluid upwards and hold it there 2. wait till it fill up 3. if it does press with 3 fingers to see if it bounds back

4. aprehension – try to push patella laterally with leg slightly bend over the edge of a table
ACL + PCL
- drawers test alternatevly
- femur stabilised on bent knee of Dr and tibia up and down
MCL + PCL
knee bent 15dgr
knee straight
ITB
Nobel test,if +ve – Ober test
Menisci
McMurray
Appley compression
Thesally – disco
Hyperextension
if P anteriorly it is Hoffa sign of fat pad impingement
Joint above and below
screening Ankle and Hip