Degenerative Disc Disease
Kettering Osteopath. Low Back Pain and Sciatica
Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease
Introduction
The intervertebral discs in the lower spine are commonly blamed for low back pain. Yet low back pain has many possible causes, and doctors aren’t always certain why symptoms occur.
During an office visit for low back pain, your doctor may describe how changes in the discs can lead to back pain. When talking about these changes, your doctor may use the terms degeneration or degenerative disc disease. Although the parts of the spine do change with time and in some sense degenerate, this does not mean the spine is deteriorating and that you are headed for future pain and problems. These terms are simply a starting point for describing what occurs in the spine over time, and how the changes may explain the symptoms people feel.
Anatomy

The human spine is made up of 24 spinal bones, called vertebrae. Vertebrae are stacked on top of one another to form the spinal column. The spinal column gives the body its form. It is the body’s main upright support. The section of the spine in the lower back is known as the lumbar spine.

An intervertebral disc sits between each pair of vertebrae. The intervertebral disc is made of connective tissue. Connective tissue is the material that holds the living cells of the body together. Most connective tissue is made of fibers of a material called collagen. These fibers help the disc withstand tension and pressure.
The disc normally works like a shock absorber. It protects the spine against the daily pull of gravity. It also protects the spine during strenuous activitiesthat put strong force on the spine, such as jumping, running, and lifting.

An intervertebral disc is made of two parts. The center, called the nucleus, is spongy providing most of the disc’s ability to absorb shock. It is held in place by the annulus, a series of strong ligament rings surrounding it. Ligaments are connective tissues that attach bones to other bones.

Between the vertebrae of each spinal segment are two facet joints. The facet joints are located on the back of the spinal column. There are two facet joints between each pair of vertebrae, one on each side of the spine. A facet joint is made of small, bony knobs that line up along the back of the spine. Where these knobs meet, they form a joint that connects the two vertebrae. The alignment of the facet joints of the lumbar spine allows freedom of movement as you bend forward and back.
Causes
Our intervertebral discs change with age, much like our hair turns gray. Conditions such as a major back injury or fracture can affect how the spine works, making the changes happen even faster. Daily wear and tear and certain types of vibration can also speed up degeneration in the spine. In addition, strong evidence suggests that smoking speeds up degeneration of the spine. Scientists have also found links among family members, showing that genetics play a role in how fast these changes occur.

Disc degeneration follows a predictable pattern. First, the nucleus in the center of the disc begins to lose its ability to absorb water. The disc becomes dehydrated. Then the nucleus becomes thick and fibrous, so that it looks much the same as the annulus. As a result, the nucleus isn’t able to absorb shock as well. Routine stress and strain begin to take a toll on the structures of the spine. Tears form around the annulus. The disc weakens. It starts to collapse, and the bones of the spine compress.
This degeneration does not always mean the disc becomes a source of pain. In fact, X-rays and MRI scans show that people with severe disc degeneration don’t always feel pain.

Pain caused by degenerative disc disease is mainly mechanical pain, meaning it comes from the parts of the spine that move during activity: the discs, ligaments, and facet joints. Movement within the weakened structures of the spine causes them to become irritated and painful.
Symptoms
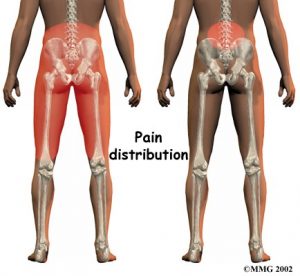
Pain in the center of the low back is often the first symptom patients feel. It usually starts to affect patients in their twenties and thirties. Pain tends to worsen after heavy physical activity or staying in one posture for a long time. The back may also begin to feel stiff. Resting the back eases pain. At first, symptoms only last a few days.
This type of back pain often comes and goes over the years. Doctors call this recurring back pain. Each time it strikes, the pain may seem worse than the time before. Eventually the pain may spread into the buttocks or thighs, and it may take longer for the pain to subside.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis begins with a complete history and physical exam. Your doctor will ask questions about your symptoms and how your problem is affecting your daily activities. Your doctor will also want to know what positions or activities make your symptoms worse or better.
Then the doctor does a physical examination by checking your posture and the amount of movement in your low back. Your doctor checks to see which back movements cause pain or other symptoms. Your skin sensation, muscle strength, and reflexes are also tested.
Doctors rely on the history and physical exam to determine which treatments will help the most. X-rays are rarely ordered on the first doctor visit for this problem. This is because over 30 percent of low back X-rays show abnormalities from degeneration, even in people who aren’t having symptoms.
However, if symptoms are severe and aren’t going away, the doctor may order an X-ray. The test can show if one or more discs has started to collapse. It can also show if there are bone spurs in the vertebrae and facet joints. Bone spurs are small points of bone that form with degeneration.
When more information is needed, your doctor may order a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan. The MRI machine uses magnetic waves rather than X-rays to show the soft tissues of the body. It is helpful for showing if the tissues in the disc are able to absorb water and whether there are cracks inside the disc. It can also show if there are problems in other soft tissues, such as the spinal nerves.
Discography can help with the diagnosis. This is a specialized X-ray test in which dye is injected into one or more discs. The dye is seen on X-ray and can give some information about the health of the disc or discs. This test may be done when the surgeon is considering surgery, since it can help determine which disc is causing the symptoms.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Whenever possible, doctors prefer treatment other than surgery. The first goal of nonsurgical treatment is to ease pain and other symptoms so the patient can resume normal activities as soon as possible.
Doctors rarely prescribe bed rest for patients with degenerative disc problems. Instead, patients are encouraged to do their normal activities using pain as a gauge for how much is too much. If symptoms are severe, a maximum of two days of bed rest may be prescribed.
Back braces are sometimes prescribed. Keeping the moving parts of the low back still can help calm mechanical pain. When a doctor issues a brace, he or she normally asks that the patient only wear it for two to four days. This lessens the chance that the trunk muscles will shrink (atrophy) from relying on the belt.
Patients may also be prescribed medication to help them gain control of their symptoms so they can resume normal activity swiftly.
If symptoms continue to limit a person’s ability to function normally, the doctor may suggest an epidural steroid injection (ESI). Steroids are powerful anti-inflammatories, meaning they help reduce pain and swelling. In an ESI, medication is injected into the space around the lumbar nerve roots. This area is called the epidural space. Some doctors inject only a steroid. Most doctors, however, combine a steroid with a long-lasting numbing medication. Generally, an ESI is given only when other treatments aren’t working. But ESIs are not always successful in relieving pain. If they do work, they often only provide temporary relief.
In addition, patients often work with a physical therapist. After evaluating a patient’s condition, the therapist can assign positions and exercises to ease symptoms. The therapist can design an exercise program to improve flexibility of tight muscles, to strengthen the back and abdominal muscles, and to help a patient move safely and with less pain.
Nonsurgical Rehabilitation
Your doctor may recommend that you work with a physical therapist a few times each week for four to six weeks. In some cases, patients may need a few additional weeks of care.
The first goal of treatment is to control symptoms. Your therapist will work with you to find positions and movements that ease pain. The therapist may use heat, cold, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation to calm pain and muscle spasm.
The therapist may perform hands-on treatments such as massage and specialized forms of soft-tissue mobilization. These can help a patient begin moving with less pain and greater ease. Spinal manipulation provides short-term relief of degenerative disc symptoms. Commonly thought of as an adjustment, spinal manipulation helps reset the sensitivity of the spinal nerves and muscles, easing pain and improving mobility. It involves a high-impulse stretch of the spinal joints and is characterized by the sound of popping as the stretch is done.
Traction is also a common treatment for degenerative disc problems. Traction gently stretches the low back joints and muscles. Patients are also shown stretches to help them move easier and with less pain.
As you recover, you will gradually advance in a series of strengthening exercises for the abdominal and low back muscles. Working these core muscles helps patients move more easily and lessens the chances of future pain and problems.
A primary purpose of therapy is to help you learn how to take care of your symptoms and prevent future problems. You’ll be given a home program of exercises to continue improving flexibility, posture, endurance, and low back and abdominal strength. The therapist will also discuss strategies you can use if your symptoms flare up.
Colgan Osteopathy in Kettering Northamptonshire
Colgan Osteopathy in Hatfield, Hertfordshire
To book an appointment, call 07738493974 or book online
