Shoulder Impingement
Colgan Osteopath in Kettering Northamptonshire
Shoulder Impingement
The shoulder is a very complex piece of machinery. Its elegant design gives the shoulder joint great range of motion, but not much stability. As long as all the parts are in good working order, the shoulder can move freely and painlessly.
Many people refer to any pain in the shoulder as bursitis. The term bursitis really only means that the part of the shoulder called the bursa is inflamed. Tendonitis is when a tendon gets inflamed. This can be another source of pain in the shoulder. Many different problems can cause inflammation of the bursa or tendons. Impingement syndrome is one of those problems. Impingement syndrome occurs when the rotator cuff tendons rub against the roof of the shoulder, the acromion.
Anatomy
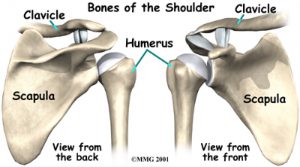
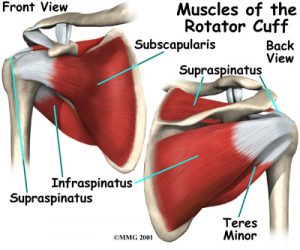
The shoulder is made up of three bones: the scapula (shoulder blade), the humerus (upper arm bone), and the clavicle (collarbone).The rotator cuff connects the humerus to the scapula. The rotator cuff is formed by the tendons of four muscles: the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis.
Tendons attach muscles to bones. Muscles move the bones by pulling on the tendons. The rotator cuff helps raise and rotate the arm.
As the arm is raised, the rotator cuff also keeps the humerus tightly in the socket of the scapula,
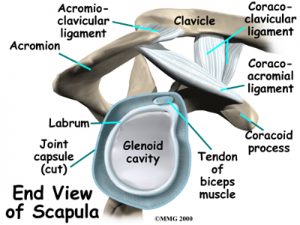
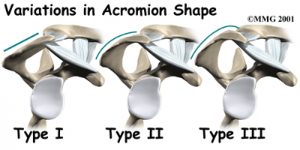
the glenoid. The upper part of the scapula that makes up the roof of the shoulder is called the acromion.
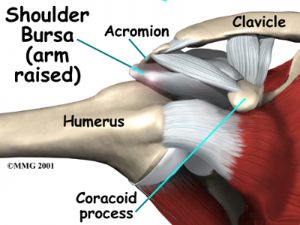
A bursa is located between the acromion and the rotator cuff tendons. A bursa is a lubricated sac of tissue that cuts down on the friction between two moving parts. Bursae are located all over the body where tissues must rub against each other. In this case, the bursa protects the acromion and the rotator cuff from grinding against each other.
Causes
Usually, there is enough room between the acromion and the rotator cuff so that the tendons slide easily underneath the acromion as the arm is raised. But each time you raise your arm, there is a bit of rubbing or pinching on the tendons and the bursa. This rubbing or pinching action is called impingement.
Impingement occuss to some degree in everyone’s shoulder. Day-to-day activities that involve using the arm above shoulder level cause some impingement. Usually it doesn’t lead to any prolonged pain. But continuously working with the arms raised overhead, repeated throwing activities, or other repetitive actions of the shoulder can cause impingement to become a problem. Impingement becomes a problem when it causes irritation or damage to the rotator cuff tendons.
Raising the arm tends to force the humerus against the edge of the acromion. With overuse, this can cause irritation and swelling of the bursa. If any other condition decreases the amount of space between the acromion and the rotator cuff tendons, the impingement may get worse.
Bone spurs can reduce the space available for the bursa and tendons to move under the acromion. Bone spurs are bony points. They are commonly caused by wear and tear of the joint between the collarbone and the scapula, called the acromioclavicular (AC) joint. The AC joint is directly above the bursa and rotator cuff tendons.
In some people, the space is too small because the acromion is oddly sized. In these people, the acromion tilts too far down, reducing the space between it and the rotator cuff.
Symptoms
Impingement syndrome causes generalized shoulder aches in the condition’s early stages. It also causes pain when raising the arm out to the side or in front of the body. Most patients complain that the pain makes it difficult for them to sleep, especially when they roll onto the affected shoulder.
A reliable sign of impingement syndrome is a sharp pain when you try to reach into your back pocket. As the condition worsens, the discomfort increases. The joint may become stiffer. Sometimes a catching sensation is felt when you lower your arm. Weakness and inability to raise the arm may indicate that the rotator cuff tendons are actually torn.
Exersices
Put the band around your wrists with your elbows extended and arms by your side.
Put a minimal amount of pressure into the band and rotate your thumbs 45° out.
Maintaining the pressure, lift your arms all the way overhead.
Do not extend your spine or thrust your chin forward.
Lower the arms to come back to the starting position and repeat.


Ref : www.eorthopod.com
Other conditions affecting shoulder
Shoulder Strengthening Exercise
Colgan Osteopathy in Kettering Northamptonshire
Colgan Osteopathy in Hatfield, Hertfordshire
To book an appointment, call 07738493974 or book online